

Plasmids are found in a few simple eukaryotic organisms.ĭNA is a single molecule, found free in the cytoplasm. There are no mitochondria or chloroplasts.ĭNA in a nucleus.
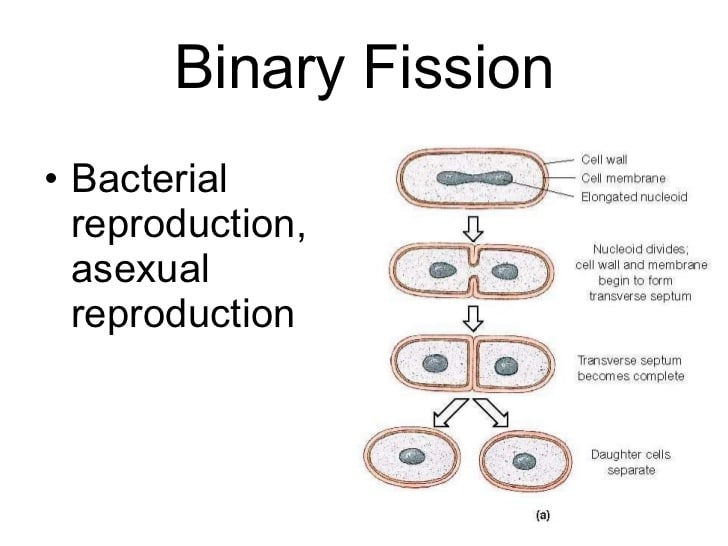
Cell organelles include mitochondria, chloroplasts in plants and ribosomes.Ĭytoplasm. Surrounded by cell wall in plants and fungi.Ĭytoplasm. The process is similar, but we use a different name for it because prokaryotic bacteria are very different from other eukaryotic plant and animal cells.Įukaryotic and prokaryotic cells can be compared: FeatureĬell membrane. Instead they copy themselves by binary fission.
Only plant cell walls are made from cellulose.īacteria are amongst the simplest of organisms. Plant and bacterial cell walls provide structure and protection. These can rotate or move in a whip-like motion to move the bacterium. Unlike the chromosomal DNA, plasmid DNA can move from one bacterium to another giving variation.īacteria can have one or more flagella (singular: flagellum). It is called chromosomal DNA and is not contained within a nucleus.īacteria also have small, closed-circles of DNA called plasmids present in their cytoplasm. The DNA of bacterial cells is found loose in the cytoplasm. Bacteria have other components that are unique: Structure These include the cytoplasm and cell membrane. Plant and animal cells have some components in common with bacterial cells. A generalised bacterial cell and its components Larger bacterial cells may be visible using a light microscope, however an electron microscope would be needed to see the details of the cell organelles. This means they do not have a nucleus or any other structures which are surrounded by membranes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
